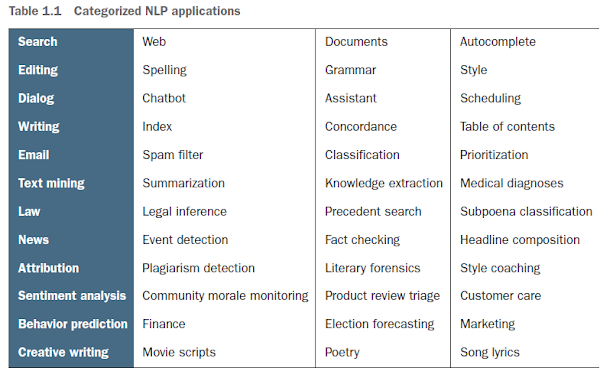
Natural language processing is everywhere. It’s so ubiquitous that some of the examples in table below may surprise you.Categorized NLP applications
A search engine can provide more meaningful results if it indexes web pages or document archives in a way that takes into account the meaning of natural language text. Autocomplete uses NLP to complete your thought and is common among search engines and mobile phone keyboards. Many word processors, browser plugins, and text editors have spelling correctors, grammar checkers, concordance composers, and most recently, style coaches. Some dialog engines (chatbots) use natural language search to find a response to their conversation partner’s message. NLP pipelines that generate (compose) text can be used not only to compose short replies in chatbots and virtual assistants, but also to assemble much longer passages of text. The Associated Press uses NLP “robot journalists” to write entire financial news articles and sporting event reports.7 Bots can compose weather forecasts that sound a lot like what your hometown weather person might say, perhaps because human meteorologists use word processors with NLP features to draft scripts. NLP spam filters in early email programs helped email overtake telephone and fax communication channels in the '90s. And the spam filters have retained their edge in the cat and mouse game between spam filters and spam generators for email, but may be losing in other environments like social networks. An estimated 20% of the tweets about the 2016 US presidential election were composed by chatbots.8 These bots amplify their owners’ and developers’ viewpoints. And these “puppet masters” tend to be foreign governments or large corporations with the resources and motivation to influence popular opinion. NLP systems can generate more than just short social network posts. NLP can be used to compose lengthy movie and product reviews on Amazon and elsewhere. Many reviews are the creation of autonomous NLP pipelines that have never set foot in a movie theater or purchased the product they’re reviewing. There are chatbots on Slack, IRC, and even customer service websites—places where chatbots have to deal with ambiguous commands or questions. And chatbots paired with voice recognition and generation systems can even handle lengthy conversations with an indefinite goal or “objective function” such as making a reservation at a local restaurant.9 NLP systems can answer phones for companies that want something better than a phone tree but don’t want to pay humans to help their customers.NOTE
With its Duplex demonstration at Google IO, engineers and managers overlooked concerns about the ethics of teaching chatbots to deceive humans. We all ignore this dilemma when we happily interact with chatbots on Twitter and other anonymous social networks, where bots don’t share their pedigree. With bots that can so convincingly deceive us, the AI control problem looms, and Yuval Harari’s cautionary forecast of “Homo Deus” may come sooner than we think. NLP systems exist that can act as email “receptionists” for businesses or executive assistants for managers. These assistants schedule meetings and record summary details in an electronic Rolodex, or CRM (customer relationship management system), interacting with others by email on their boss’s behalf. Companies are putting their brand and face in the hands of NLP systems, allowing bots to execute marketing and messaging campaigns. And some inexperienced daredevil NLP textbook authors are letting bots author several sentences in their book.
Pages
- Index of Lessons in Technology
- Index of Book Summaries
- Index of Book Lists And Downloads
- Index For Job Interviews Preparation
- Index of "Algorithms: Design and Analysis"
- Python Course (Index)
- Data Analytics Course (Index)
- Index of Machine Learning
- Postings Index
- Index of BITS WILP Exam Papers and Content
- Lessons in Investing
- Index of Math Lessons
- Index of Management Lessons
- Book Requests
- Index of English Lessons
- Index of Medicines
- Index of Quizzes (Educational)
Saturday, July 2, 2022
Practical applications of Natural Language Processing
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment