Download XLSX files from the trainings
Pages
- Index of Lessons in Technology
- Index of Book Summaries
- Index of Book Lists And Downloads
- Index For Job Interviews Preparation
- Index of "Algorithms: Design and Analysis"
- Python Course (Index)
- Data Analytics Course (Index)
- Index of Machine Learning
- Postings Index
- Index of BITS WILP Exam Papers and Content
- Lessons in Investing
- Index of Math Lessons
- Downloads
- Index of Management Lessons
- Book Requests
- Index of English Lessons
- Index of Medicines
- Index of Quizzes (Educational)
Showing posts with label Cloud. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Cloud. Show all posts
Sunday, June 27, 2021
Friday, June 11, 2021
Quick Setup Tips by GitHub itself
Wednesday, June 2, 2021
Command 'git clone'
Cloning a repository with only the URL
(base) ~\ws>git clone https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... Logon failed, use ctrl+c to cancel basic credential prompt. Username for 'https://github.com': ashishjain1547@gmail.com Password for 'https://ashishjain1547@gmail.com@github.com': remote: Enumerating objects: 16, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (16/16), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (9/9), done. remote: Total 16 (delta 5), reused 10 (delta 3), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (16/16), 5.70 KiB | 12.00 KiB/s, done. (base) ~\ws>tree /f Folder PATH listing for volume Windows Volume serial number is 8139-90C0 C:. └───repo_for_testing .gitignore LICENSE newFile.txt README.md test_file_20210528.txt (base) ~\ws>cd repo_for_testing (base) ~\ws\repo_for_testing>git branch * main (base) ~\ws\repo_for_testing>git branch -a * main remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch (base) ~\ws\repo_for_testing>git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch (base) ~\ws\repo_for_testing>git branch -D fatal: branch name requiredCloning a repository with URL and branch name.
(base) ~\ws_diff_branch>git clone --branch test_branch https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... remote: Enumerating objects: 16, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (16/16), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (9/9), done. remote: Total 16 (delta 5), reused 10 (delta 3), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (16/16), 5.70 KiB | 8.00 KiB/s, done. (base) ~\ws_diff_branch>cd repo_for_testing (base) ~\ws_diff_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch * test_branch (base) ~\ws_diff_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch -a * test_branch remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch (base) ~\ws_diff_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branchNotes From Bitbucket
#1 Cloning to a specific folder git clone <repo> <directory> Clone the repository located at <repo> into the folder called ~<directory>! on the local machine. #2 Cloning a specific tag git clone --branch <tag> <repo> Clone the repository located at <repo> and only clone the ref for <tag>. #3 Shallow clone git clone -depth=1 <repo> Clone the repository located at <repo> and only clone the history of commits specified by the option depth=1. In this example a clone of <repo> is made and only the most recent commit is included in the new cloned Repo. Shallow cloning is most useful when working with repos that have an extensive commit history. An extensive commit history may cause scaling problems such as disk space usage limits and long wait times when cloning. A Shallow clone can help alleviate these scaling issues. Ref: Bitbucket [20210602] Tags: Technology,GitHub,Cloud,Windows CMD,
Thursday, May 27, 2021
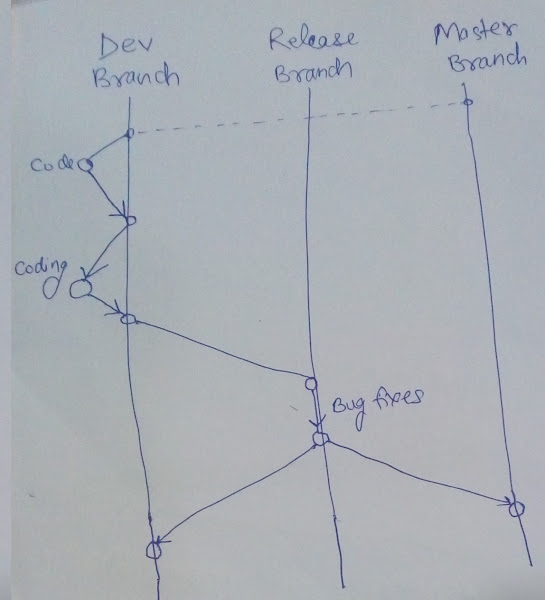
Introduction to GitHub branching in 10 commands
Introduction to GitHub branching in 10 commands: 1. git clone [repo_url] 2. git branch [-r] [-a] 3. git branch --set-upstream-to 4. git pull 5. git checkout [-b] [branch_name] 6. git push origin HEAD:[branch_name] 7. git switch -c [branch_name] 8. git log 9. git clone --branch [branch_name] [repo_url] 10. git push --set-upstream origin [branch_name] Why concept of branching using an image: Now the commands:1. INITIAL SETUP USING "git clone"
CMD>git clone https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... Logon failed, use ctrl+c to cancel basic credential prompt. Username for 'https://github.com': aj@gmail.com Password for 'https://aj@gmail.com@github.com': remote: Enumerating objects: 8, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (8/8), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done. remote: Total 8 (delta 1), reused 4 (delta 1), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (8/8), 4.98 KiB | 10.00 KiB/s, done. CMD>dir /b repo_for_testing CMD>cd repo_for_testing CMD\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore LICENSE newFile.txt README.md CMD\repo_for_testing> type newFile.txt NEWFILE2. LIST ALL THE BRANCHES
git branch: shows the local branches git branch -r: shows the remote branches git branch -a: shows all the branches (both local and remote) ~\aj> git clone https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... remote: Enumerating objects: 14, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (14/14), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done. remote: Total 14 (delta 4), reused 8 (delta 2), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (14/14), 5.41 KiB | 5.00 KiB/s, done. ~\aj> cd repo_for_testing ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch * main ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -a * main remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git checkout -b test_branch Switched to a new branch 'test_branch' Note: If you already have a branch named "test_branch" in your local, then you would not pass the argument "-b". ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch main * test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch Note: we would not see any changes in the remote branches from "git checkout" command. ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -a main * test_branch remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch3. SUPPOSE YOUR NEW REMOTE BRANCH IS NOT VISIBLE IN CMD USING "git branch -r", THEN TO LOAD NEW REMOTE BRANCH TO SHOW UP IN AN EXISTING LOCAL REPO, DO A 'GIT PULL'
CMD\repo_for_testing> git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main CMD\repo_for_testing> git pull From https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing * [new branch] test_branch -> origin/test_branch Already up to date. CMD\repo_for_testing> git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch4. CREATING A NEW LOCAL BRANCH 'test_branch', SETTING UPSTREAM BRANCH FOR IT AND ADDING A NEW FILE IN IT
~\aj> git clone https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... remote: Enumerating objects: 19, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (19/19), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (11/11), done. remote: Total 19 (delta 6), reused 12 (delta 3), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (19/19), 5.92 KiB | 6.00 KiB/s, done. ~\aj> cd repo_for_testing ~\aj\repo_for_testing>git branch * main ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -a * main remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch 'git checkout -b test_branch' CREATES A NEW LOCAL BRANCH NAMED 'test_branch' BECAUSE OF THE ARGUMENT '-b' ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git checkout -b test_branch Switched to a new branch 'test_branch' ~\aj\repo_for_testing>git branch main * test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing>git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch -a main * test_branch remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/main remotes/origin/main remotes/origin/test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> dir Volume in drive C is Windows Volume Serial Number is 8139-90C0 Directory of ~\aj\repo_for_testing 07/14/2021 04:06 PM DIR> . 07/14/2021 04:06 PM DIR> .. 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 368 .gitignore 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 11,558 LICENSE 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 11 newFile.txt 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 38 README.md 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 23 test_file_20210528.txt 5 File(s) 11,998 bytes 2 Dir(s) 62,644,645,888 bytes free ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/test_branch test_branch Branch 'test_branch' set up to track remote branch 'test_branch' from 'origin'. ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git pull Updating daa4600..82c204f Fast-forward 20210528_test_branch.txt | 1 + 202107141543.txt | 1 + 2 files changed, 2 insertions(+) create mode 100644 20210528_test_branch.txt create mode 100644 202107141543.txt ~\aj\repo_for_testing> echo "202107141608" > 202107141608.txt ~\aj\repo_for_testing> dir Volume in drive C is Windows Volume Serial Number is 8139-90C0 Directory of ~\aj\repo_for_testing 07/14/2021 04:08 PM DIR> . 07/14/2021 04:08 PM DIR> .. 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 368 .gitignore 07/14/2021 04:08 PM 30 20210528_test_branch.txt 07/14/2021 04:08 PM 17 202107141543.txt 07/14/2021 04:08 PM 17 202107141608.txt 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 11,558 LICENSE 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 11 newFile.txt 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 38 README.md 07/14/2021 04:06 PM 23 test_file_20210528.txt 8 File(s) 12,062 bytes 2 Dir(s) 62,644,277,248 bytes free ~\aj\repo_for_testing>git status On branch test_branch Your branch is up to date with 'origin/test_branch'. Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) 202107141608.txt nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track) ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git add -A ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git commit -m "#" [test_branch 9017804] # 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 202107141608.txt ~\aj\repo_for_testing> git push Enumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 284 bytes | 142.00 KiB/s, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object. To https://github.com/ashishjain1547/repo_for_testing.git 82c204f..9017804 test_branch -> test_branch ~\aj\repo_for_testing> Note: Now, you can go to GitHub.com and create a pull request, then merge "test_branch" with "main" branch.5. SWITCHING TO THE NEW BRANCH
CMD\repo_for_testing> git checkout origin/test_branch Note: switching to 'origin/test_branch'. You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch. If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example: git switch -c [new-branch-name] Or undo this operation with: git switch - Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false HEAD is now at 5b934da cmt 1909 CMD\repo_for_testing>git branch * (HEAD detached at origin/test_branch) main ~ ~ ~ Use the '-b' argument to also attach the HEAD to new branch. CMD\repo_for_testing> git checkout -b origin/test_branch Switched to a new branch 'origin/test_branch' CMD\repo_for_testing> git branch main * origin/test_branch 6. ADDING A FILE TO THE NEW BRANCH CMD\repo_for_testing> echo "20210528 into test_branch" > "20210528_test_branch.txt" CMD\repo_for_testing> dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md CMD\repo_for_testing> git status HEAD detached at origin/test_branch Untracked files: (use "git add [file]..." to include in what will be committed) 20210528_test_branch.txt nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track) CMD\repo_for_testing> git add -A CMD\repo_for_testing> git commit -m "0303" [detached HEAD 03e190f] 0303 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 20210528_test_branch.txt CMD\repo_for_testing>git push fatal: You are not currently on a branch. To push the history leading to the current (detached HEAD) state now, use git push origin HEAD:[name-of-remote-branch] CMD\repo_for_testing> git push origin HEAD:test_branch Enumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 306 bytes | 306.00 KiB/s, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object. To https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git 5b934da..03e190f HEAD -> test_branch7. CHECKING REPOSITORY STATUS USING 'GIT LOG'
CMD\repo_for_testing> git log In the logs below, "HEAD" is detached. commit 03e190f8810c9335613cc2c534914e666c04eeeb (HEAD, origin/test_branch) Author: unknown [abc@xyz.com] Date: Fri May 28 03:03:23 2021 +0530 0303 commit 5b934dac6c399f06275feab5b4a91fa8063e092b (origin/main, origin/HEAD, main) Author: Admin on Ubuntu [admin@master.com] Date: Wed Mar 17 19:09:57 2021 +0530 cmt 1909 commit 974a71b3df68140ebbc3b4775201b39c500aa589 Author: aj [abc@xyz.com] Date: Wed Mar 17 01:32:16 2021 +0530 Initial commit Fixing the detached HEAD: CMD\repo_for_testing>git switch -c origin/test_branch Switched to a new branch 'origin/test_branch' CMD\repo_for_testing>git branch main * origin/test_branch Now the HEAD is pointing to the current branch: CMD\repo_for_testing> git log commit 03e190f8810c9335613cc2c534914e666c04eeeb (HEAD -> origin/test_branch, origin/test_branch) Author: unknown [abc@xyz.com] Date: Fri May 28 03:03:23 2021 +0530 0303 commit 5b934dac6c399f06275feab5b4a91fa8063e092b (origin/main, origin/HEAD, main) Author: Admin on Ubuntu [admin@master.com] Date: Wed Mar 17 19:09:57 2021 +0530 cmt 1909 commit 974a71b3df68140ebbc3b4775201b39c500aa589 Author: aj [abc@xyz.com] Date: Wed Mar 17 01:32:16 2021 +0530 Initial commit8. USING 'GIT CLONE' TO CLONE A BRANCH
CMD\ws_branches\(2)> git clone --branch test_branch https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... remote: Enumerating objects: 11, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (11/11), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (6/6), done. remote: Total 11 (delta 2), reused 7 (delta 2), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (11/11), 5.23 KiB | 3.00 KiB/s, done. CMD\ws_branches\(2)>cd repo_for_testing CMD\ws_branches\(2)\repo_for_testing>git branch * test_branch CMD\ws_branches\(2)\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md9. NOW WE ADD A NEW FILE TO THE 'main' BRANCH
~\ws_branches\(3) main branch> git clone https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git Cloning into 'repo_for_testing'... remote: Enumerating objects: 11, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (11/11), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (6/6), done. remote: Total 11 (delta 2), reused 7 (delta 2), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (11/11), 5.23 KiB | 3.00 KiB/s, done. ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch>cd repo_for_testing ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore LICENSE newFile.txt README.md ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>echo "test_file_20210528" > "test_file_20210528.txt" ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore LICENSE newFile.txt README.md test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>git add -A ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>git commit -m "0357" [main daa4600] 0357 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>git push Enumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 298 bytes | 298.00 KiB/s, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object. To https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git 5b934da..daa4600 main -> main ~\ws_branches\(3) main branch\repo_for_testing>10. NEXT, WE GET THAT NEW FILE INTO OUR 'test_branch'
~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch * test_branch ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git fetch remote: Enumerating objects: 4, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1/1), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 1), reused 3 (delta 1), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 278 bytes | 2.00 KiB/s, done. From https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing 5b934da..daa4600 main -> origin/main ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/main origin/main origin/test_branch ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing> git checkout origin/main Note: switching to 'origin/main'. You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch. If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example: git switch -c <new-branch-name> Or undo this operation with: git switch - Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false HEAD is now at daa4600 0357 ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git switch -c origin/main Switched to a new branch 'origin/main' ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch * origin/main test_branch ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore LICENSE newFile.txt README.md test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing> git pull There is no tracking information for the current branch. Please specify which branch you want to merge with. See git-pull(1) for details. git pull <remote> <branch> If you wish to set tracking information for this branch you can do so with: git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/<branch> origin/main ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git pull https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git origin/main fatal: couldn't find remote ref origin/main ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/test_branch origin/main Branch 'origin/main' set up to track remote branch 'test_branch' from 'origin'. ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git pull Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy. 20210528_test_branch.txt | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 20210528_test_branch.txt ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git checkout origin/test_branch Note: switching to 'origin/test_branch'. You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch. If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example: git switch -c <new-branch-name> Or undo this operation with: git switch - Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false HEAD is now at 03e190f 0303 ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git switch -c origin/test_branch Switched to a new branch 'origin/test_branch' ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git switch -c origin/main fatal: A branch named 'origin/main' already exists. ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git merge origin/main warning: refname 'origin/main' is ambiguous. warning: refname 'origin/main' is ambiguous. Updating 03e190f..fca45d6 Fast-forward test_file_20210528.txt | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git push fatal: The current branch origin/test_branch has no upstream branch. To push the current branch and set the remote as upstream, use git push --set-upstream origin origin/test_branch CMD\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git push --set-upstream origin origin/test_branch This step might have been wrong w.r.t. the input argument above. The command should have been: git push --set-upstream origin test_branch Enumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (2/2), 354 bytes | 354.00 KiB/s, done. Total 2 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object. remote: remote: Create a pull request for 'origin/test_branch' on GitHub by visiting: remote: https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing/pull/new/origin/test_branch remote: To https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing.git * [new branch] origin/test_branch -> origin/test_branch Branch 'origin/test_branch' set up to track remote branch 'origin/test_branch' from 'origin'. ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>dir /b .gitignore 20210528_test_branch.txt LICENSE newFile.txt README.md test_file_20210528.txt ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch origin/main * origin/test_branch test_branch ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git branch -r origin/HEAD -> remotes/origin/main origin/main origin/origin/test_branch origin/test_branch ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing>git log commit fca45d643326fb5d88d70c0cf699f7032118df4b (HEAD -> origin/test_branch, origin/origin/test_branch, origin/main) Merge: daa4600 03e190f Author: unknown <aj@gmail.com> Date: Fri May 28 04:02:07 2021 +0530 Merge branch 'test_branch' of https://github.com/aj/repo_for_testing into origin/main commit daa46003a895e4b33577e3c248977334620e3558 (origin/main, origin/HEAD) Author: unknown <aj@gmail.com> Date: Fri May 28 03:57:24 2021 +0530 0357 commit 03e190f8810c9335613cc2c534914e666c04eeeb (origin/test_branch, test_branch) Author: unknown <aj@gmail.com> Date: Fri May 28 03:03:23 2021 +0530 0303 commit 5b934dac6c399f06275feab5b4a91fa8063e092b Author: Admin on Ubuntu <administrator@master.com> Date: Wed Mar 17 19:09:57 2021 +0530 cmt 1909 commit 974a71b3df68140ebbc3b4775201b39c500aa589 Author: aj <aj@gmail.com> Date: Wed Mar 17 01:32:16 2021 +0530 Initial commit ~\ws_branches\(2) test_branch\repo_for_testing> Tags: Technology,GitHub,Cloud,
Friday, May 21, 2021
Activating MFA on GitHub and also PAT [May 2021]
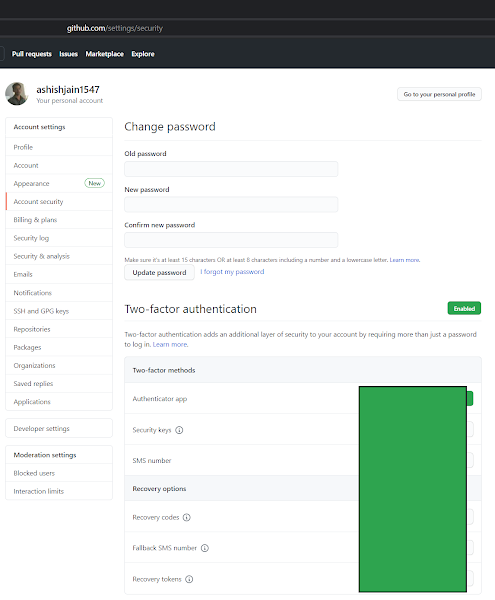
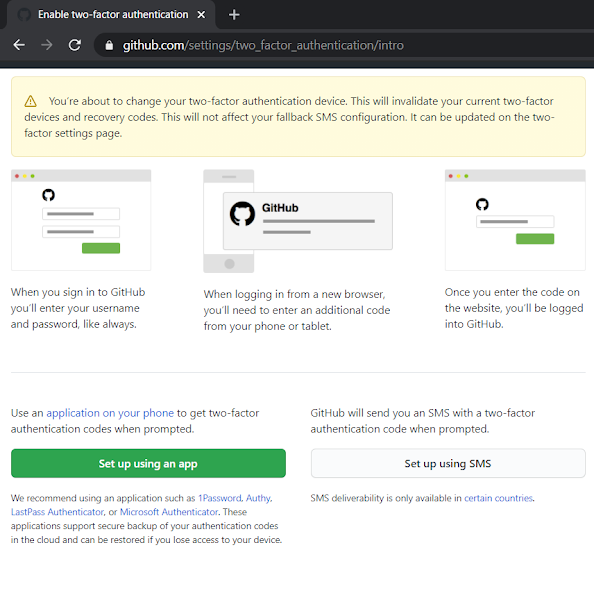
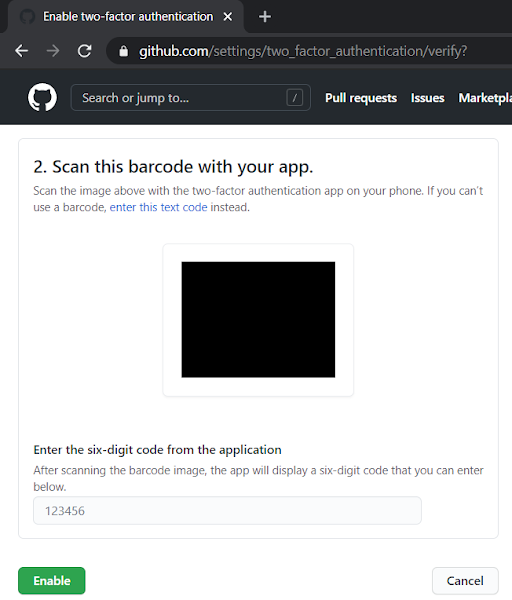
Log into GitHub account and follow the screenshots: I1 - Go to Account Security: github.com/settings/security I2 - GitHub MFA using Authenticator App I3 - GitHub asks you to scan a barcode and provide 6-digit code from the Authenticator app I4 - Microsoft Authenticator App (Download Screenshot) I5 - Manage MFA - Recovery Options [URL: github.com/settings/two_factor_authentication/configure ] I6 - Also make sure to set up: Personal Access Tokens [URL: github.com/settings/tokens] Tags: Cloud, Cyber Security, Technology,GitHub,
What is GitHub
GitHub, Inc. is a provider of Internet hosting {1} for software development {2} and version control {3} using Git {4}. It offers the distributed version control {5} and source code management (SCM) {3} functionality of Git, plus its own features. It provides access control {6} and several collaboration features such as bug tracking {7}, feature requests {8}, task management {9}, continuous integration {10} and wikis {11} for every project.
Headquartered in California, it has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018.
GitHub offers its basic services free of charge. Its more advanced professional and enterprise services are commercial. Free GitHub accounts are commonly used to host open-source {12} projects.
2019: As of January 2019, GitHub offers unlimited private repositories {13} to all plans, including free accounts, but allowed only up to three collaborators per repository for free.
2020: Starting from April 15, 2020, the free plan allows unlimited collaborators, but restricts private repositories to 2,000 minutes of GitHub Actions {14} per month.
As of January 2020, GitHub reports having over 40 million users and more than 190 million repositories (including at least 28 million public repositories), making it the largest host of source code {15} in the world.
Wikipedia Card
Type of business: Subsidiary
Type of site: Collaborative version control
Available in: English
Founded: February 8, 2008; 13 years ago (as Logical Awesome LLC)
Headquarters: San Francisco, California, United States
Area served: Worldwide
Founder(s):
#1 Tom Preston-Werner
#2 Chris Wanstrath
#3 P. J. Hyett
#4 Scott Chacon
Key people:
CEO: Nat Friedman
CFO: Mike Taylor
Industry:
#1 Collaborative version control (GitHub)
#2 Blog host (GitHub Pages)
#3 Package repository (NPM)
Revenue: Increase $300 million (2018)
Employees: 1677
Parent: Microsoft
URL: github.com
Registration: Optional (required for creating and joining repositories)
Users: 56 million (as of September 2020)
Launched: April 10, 2008; 13 years ago
Current status: Active
Written in:
#1 Ruby
#2 ECMAScript
#3 Go
#4 C
Git-SCM
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
Git is easy to learn and has a tiny footprint with lightning fast performance. It outclasses SCM tools like Subversion, CVS, Perforce, and ClearCase with features like cheap local branching, convenient staging areas, and multiple workflows.
Ref: git-scm
Keywords
1. Internet hosting
An Internet hosting service is a service that runs servers connected to the Internet, allowing organizations and individuals to serve content or host services connected to the Internet.
A common kind of hosting is web hosting. Most hosting providers offer a combination of services - e-mail hosting, website hosting, and database hosting, for example. DNS hosting service, another type of service usually provided by hosting providers, is often bundled with domain name registration.
Dedicated server hosts, provide a server, usually housed in a datacenter and connected to the Internet where clients can run anything they want (including web servers and other servers). The hosting provider ensures that the servers have Internet connections with good upstream bandwidth and reliable power sources.
Another popular kind of hosting service is shared hosting. This is a type of web hosting service, where the hosting provider provisions hosting services for multiple clients on one physical server and shares the resources between the clients. Virtualization is key to making this work effectively.
Internet hosting
2. Software Development
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development is a process of writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all that is involved between the conception of the desired software through to the final manifestation of the software, sometimes in a planned and structured process. Therefore, software development may include research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products.
The software can be developed for a variety of purposes, the three most common being to meet specific needs of a specific client/business (the case with custom software), to meet a perceived need of some set of potential users (the case with commercial and open source software), or for personal use (e.g. a scientist may write software to automate a mundane task). Embedded software development, that is, the development of embedded software, such as used for controlling consumer products, requires the development process to be integrated with the development of the controlled physical product. System software underlies applications and the programming process itself, and is often developed separately.
The need for better quality control of the software development process has given rise to the discipline of software engineering, which aims to apply the systematic approach exemplified in the engineering paradigm to the process of software development.
There are many approaches to software project management, known as software development life cycle models, methodologies, processes, or models. The waterfall model is a traditional version, contrasted with the more recent innovation of agile software development.
Software development
3. Version control
In software engineering, version control (also known as revision control, source control, or source code management) is a class of systems responsible for managing changes to computer programs, documents, large web sites, or other collections of information. Version control is a component of software configuration management.
Changes are usually identified by a number or letter code, termed the "revision number", "revision level", or simply "revision". For example, an initial set of files is "revision 1". When the first change is made, the resulting set is "revision 2", and so on. Each revision is associated with a timestamp and the person making the change. Revisions can be compared, restored, and with some types of files, merged.
The need for a logical way to organize and control revisions has existed for almost as long as writing has existed, but revision control became much more important, and complicated, when the era of computing began. The numbering of book editions and of specification revisions are examples that date back to the print-only era. Today, the most capable (as well as complex) revision control systems are those used in software development, where a team of people may concurrently make changes to the same files.
Version control systems (VCS) are most commonly run as stand-alone applications, but revision control is also embedded in various types of software such as word processors and spreadsheets, collaborative web docs[2] and in various content management systems, e.g., Wikipedia's page history. Revision control allows for the ability to revert a document to a previous revision, which is critical for allowing editors to track each other's edits, correct mistakes, and defend against vandalism and spamming in wikis.
Version control
4. Git
Git (/ɡɪt/) is software for tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows (thousands of parallel branches running on different systems).
Git was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 for development of the Linux kernel, with other kernel developers contributing to its initial development. Since 2005, Junio Hamano has been the core maintainer. As with most other distributed version control systems, and unlike most client–server systems, every Git directory on every computer is a full-fledged repository with complete history and full version-tracking abilities, independent of network access or a central server. Git is free and open-source software distributed under GNU General Public License Version 2.
Git
5. Distributed version control
In software development, distributed version control (also known as distributed revision control) is a form of version control in which the complete codebase, including its full history, is mirrored on every developer's computer. Compared to centralized version control, this enables automatic management branching and merging, speeds up most operations (except pushing and pulling), improves the ability to work offline, and does not rely on a single location for backups. Git, the world's most popular version control system, is a distributed version control system.
In 2010, software development author Joel Spolsky described distributed version control systems as "possibly the biggest advance in software development technology in the past ten years".
Distributed version control
6. Access control
In the fields of physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the selective restriction of access to a place or other resource while access management describes the process. The act of accessing may mean consuming, entering, or using. Permission to access a resource is called authorization.
Locks and login credentials are two analogous mechanisms of access control.
Access control
7. Bug tracking system
A bug tracking system or defect tracking system is a software application that keeps track of reported software bugs in software development projects. It may be regarded as a type of issue tracking system.
Many bug tracking systems, such as those used by most open-source software projects, allow end-users to enter bug reports directly. Other systems are used only internally in a company or organization doing software development. Typically bug tracking systems are integrated with other project management software.
A bug tracking system is usually a necessary component of a professional software development infrastructure, and consistent use of a bug or issue tracking system is considered one of the "hallmarks of a good software team".
Bug tracking system
8. Software feature
In software, a feature has several definitions. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers defines the term feature in IEEE 829 as "A distinguishing characteristic of a software item (e.g., performance, portability, or functionality)."
Software feature
9. Task management
Task management is the process of managing a task through its life cycle. It involves planning, testing, tracking, and reporting. Task management can help either individual achieve goals, or groups of individuals collaborate and share knowledge for the accomplishment of collective goals. Tasks are also differentiated by complexity, from low to high.
Effective task management requires managing all aspects of a task, including its status, priority, time, human and financial resources assignments, recurrence, dependency, notifications and so on. These can be lumped together broadly into the basic activities of task management.
Managing multiple individuals or team tasks may be assisted by specialized software, for example workflow or project management software.
Task management may form part of project management and process management and can serve as the foundation for efficient workflow in an organization. Project managers adhering to task-oriented management have a detailed and up-to-date project schedule, and are usually good at directing team members and moving the project forward.
Task management
10. Continuous integration
In software engineering, continuous integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developers' working copies to a shared mainline several times a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in his 1991 method, although he did not advocate integrating several times a day. Extreme programming (XP) adopted the concept of CI and did advocate integrating more than once per day – perhaps as many as tens of times per day.
Continuous integration
11. Wiki
A wiki (/ˈwɪki/ WIK-ee) is a hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience directly using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base.
Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are open source, whereas others are proprietary. Some permit control over different functions (levels of access); for example, editing rights may permit changing, adding, or removing material. Others may permit access without enforcing access control. Other rules may be imposed to organize content.
The online encyclopedia project, Wikipedia, is the most popular wiki-based website, and is one of the most widely viewed sites in the world, having been ranked in the top twenty since 2007. Wikipedia is not a single wiki but rather a collection of hundreds of wikis, with each one pertaining to a specific language. In addition to Wikipedia, there are hundreds of thousands of other wikis in use, both public and private, including wikis functioning as knowledge management resources, notetaking tools, community websites, and intranets. The English-language Wikipedia has the largest collection of articles: as of February 2020, it has over 6 million articles. Ward Cunningham, the developer of the first wiki software, WikiWikiWeb, originally described wiki as "the simplest online database that could possibly work." "Wiki" is a Hawaiian word meaning "quick."
Wiki
12. Open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. It most commonly refers to the open-source model, in which open-source software or other products are released under an open-source license as part of the open-source-software movement. Use of the term originated with software, but has expanded beyond the software sector to cover other open content and forms of open collaboration.
Open source
13. Repository (version control)
In revision control systems, a repository is a data structure that stores metadata for a set of files or directory structure. Depending on whether the version control system in use is distributed like (Git or Mercurial) or centralized like (Subversion, CVS, or Perforce), the whole set of information in the repository may be duplicated on every user's system or may be maintained on a single server. Some of the metadata that a repository contains includes, among other things:
13.1. A historical record of changes in the repository.
13.2. A set of commit objects.
13.3. A set of references to commit objects, called heads.
Repository (version control)
14. GitHub Actions
Automate your workflow from idea to production.
GitHub Actions makes it easy to automate all your software workflows, now with world-class CI/CD. Build, test, and deploy your code right from GitHub. Make code reviews, branch management, and issue triaging work the way you want.
Ref 15.1: GitHub Actions
Automate, customize, and execute your software development workflows right in your repository with GitHub Actions. You can discover, create, and share actions to perform any job you'd like, including CI/CD, and combine actions in a completely customized workflow.
Ref 15.2: GitHub Actions - Docs
Ref 15.3: YouTube
15. Source code
In computing, source code is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source code. The source code is often transformed by an assembler or compiler into binary machine code that can be executed by the computer. The machine code might then be stored for execution at a later time. Alternatively, source code may be interpreted and thus immediately executed.
Most application software is distributed in a form that includes only executable files. If the source code were included it would be useful to a user, programmer or a system administrator, any of whom might wish to study or modify the program.
Source code
Tags: Technology,Cloud,GitHub,
Activating MFA on Heroku (May 2021)
1 - MFA on Heroku (a Salesforce company) 2 - Connect an Authenticator app 3 - Microsoft Authenticator App (Download Screenshot) 4 - Heroku screen after multifactor authentication is done Tags: Cyber Security,Cloud,Technology,
Saturday, May 8, 2021
Polymorphism in Google Drive and Google Chrome (wrt Handling an Exe File)
Important Note: We are not trying to arrive at a very concrete conclusion or result here. The testing was done to identify the behavior of 'Google Drive' and 'Google Chrome' when 'Google Drive' thinks a file could be a virus. User1: This user is the original author of the file and has shared the folder with User2. 1 - incognito, no-user, two virus alerts 2 - incognito, no user - A virus was detected you can't download this file (gmat2.zip) 3 - incognito, User2, virus detected, can't download 4 - incognito, User2, polymorphism, cannot delete file in shared folder from other person 5 - normal view, User1, file with virus alert can still be downloaded from original author's account 6 - incognito, User2, different type of alert for an exe file that gdrive says could be virus but did not alert before 7 - incognito, User2, can't download file, enable third-party cookies for GDrive 8 - normal view, User1, original author can remove a file from folder shared by him 9 - inconito firefox, User2, potentially infected exe file not downloadable from incognito chrome is allowed to be downloaded here 10 - a view of gdrive trash of original author User1 with removed files 11 - incognito, User2, you do not get remove rights on a file but you do get remove rights on the entire directory shared with you 12 - Incognito chrome, User2, Still cannot download the suspected folder, asks to enable third party cookies The Files That Were Causing Virus Alerts in Google Drive When Scanned on Windows 10's 'Anti-Virus Defender' Did Not Produce Alert List View: 1 ~\110809IMS_Student_CD_Setup.exe ~\files.html ~\gmat1 ~\gmat1.zip ~\gmat2 ~\gmat2.zip ~\gmat1\gmat1mx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat1vx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat2mx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat2vx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat3mx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat3vx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat4mx.exe ~\gmat1\gmat4vx.exe ~\gmat2\gmat5mx.exe ~\gmat2\gmat5vx.exe List View: 2 Volume in drive C is Windows Volume Serial Number is 8139-90C0 Directory of ~ 05/08/2021 10:00 PM <DIR> . 05/08/2021 10:00 PM <DIR> .. 05/08/2021 09:12 PM 42,742,301 110809IMS_Student_CD_Setup.exe 05/08/2021 10:00 PM 766 files.html 05/08/2021 10:00 PM 0 files2.html 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> gmat1 05/08/2021 08:49 PM 880,985 gmat1.zip 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> gmat2 05/08/2021 01:01 PM 210,131 gmat2.zip 5 File(s) 43,834,183 bytes Directory of ~\gmat1 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> . 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> .. 10/30/2000 05:41 PM 486,400 gmat1mx.exe 03/21/2001 01:29 AM 504,320 gmat1vx.exe 05/17/2001 09:21 PM 418,816 gmat2mx.exe 03/29/2001 07:54 PM 501,760 gmat2vx.exe 05/17/2001 09:18 PM 424,448 gmat3mx.exe 03/09/2001 11:17 AM 485,376 gmat3vx.exe 05/17/2001 09:27 PM 432,128 gmat4mx.exe 03/21/2001 01:35 AM 631,808 gmat4vx.exe 8 File(s) 3,885,056 bytes Directory of ~\gmat2 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> . 05/08/2021 08:52 PM <DIR> .. 05/17/2001 09:32 PM 425,984 gmat5mx.exe 03/09/2001 11:47 AM 486,912 gmat5vx.exe 2 File(s) 912,896 bytes Total Files Listed: 15 File(s) 48,632,135 bytes 8 Dir(s) 70,736,945,152 bytes free Tags: Technology,Cyber Security,Cloud,
Monday, May 3, 2021
First time with 'Git LFS' (Git for Large Files)
Notice how our "git push" fails due to the presence of a file larger than 100MB:
(base) \gh\vid3>git push
Logon failed, use ctrl+c to cancel basic credential prompt.
Username for 'https://github.com': a@b.c
Password for 'https://a@b.c@github.com':
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
error: RPC failed; curl 92 HTTP/2 stream 0 was not closed cleanly: Unknown error code (err 8)
Wfatal: the remote end hung up unexpectedly
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 533.93 MiB | 8.86 MiB/s, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
fatal: the remote end hung up unexpectedly
Everything up-to-date
To overcome this, we install: git-lfs-windows-v2.13.2.exe
And run the following commands:
(base) \gh\vid3>git lfs install
Updated git hooks.
Git LFS initialized.
(base) \gh\vid3>git lfs track "*.*"
Tracking "*.*"
Pattern *.* matches forbidden file .gitignore. If you would like to track .gitignore, modify .gitattributes manually.
(base) \gh\vid3> git lfs track "*.mp4"
Tracking "*.mp4"
(base) \gh\vid3>git add .gitattributes
Note: if we do not do "add & commit" again before "push" again, it results in error:
(base) \gh\vid3>git push
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
error: RPC failed; curl 92 HTTP/2 stream 0 was not closed cleanly: Unknown error code (err 8)
Wfatal: the remote end hung up unexpectedly
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 533.93 MiB | 8.37 MiB/s, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
fatal: the remote end hung up unexpectedly
Everything up-to-date
After we rename files, add and commit them:
(base) \gh\vid3>git status
On branch main
Your branch is ahead of 'origin/main' by 1 commit.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: .gitattributes
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: 20210420 174746.mp4
deleted: 20210420_174746.mp4
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
20210420 174746 (27 MB).mp4
20210420 174746 (521 MB).mp4
If you have low network speed, your "git push" might fail like this:
(base) \gh\vid3>git push
LFS: Client error: https://github-cloud.s3.amazonaws.com/alambic/media/3...2/0f/65/0...f?actor_id=8...7&key_id=0&repo_id=3...1
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://github.com/ashishjainblogger/vid3.git'
(base) \gh\vid3>git push
Uploading LFS objects: 67% (2/3), 98 MB | 105 KB/s
Exiting because of "interrupt" signal.
Additional Note:
My Airtel 4G VoLTE Mobile Hotspot (May 2021) was giving an upload speed of roughly 100 to 200 KB/s.
If everything about the Git-LFS goes right
(base) C:\Users\Ashish Jain\OneDrive\Desktop\gh\vid3>git push
Uploading LFS objects: 67% (2/3), 91 MB | 107 KB/s
A successful attempt logs go like this:
(base) \gh\vid3>git push
Uploading LFS objects: 100% (1/1), 27 MB | 0 B/s, done.
Enumerating objects: 7, done.
Counting objects: 100% (7/7), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Writing objects: 100% (6/6), 713 bytes | 237.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 6 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), done.
To https://github.com/ashishjainblogger/vid3.git
2*a..e*7 main -> main
[ Ref ]
Title: First time with 'Git LFS' (Git for Large Files)
Tags: Technology,GitHub,Cloud,
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)